A staggering 76% of IT recruiters report difficulties attracting qualified candidates, highlighting the urgent need for innovative talent acquisition strategies. This shortage, coupled with the increasing demand for software solutions, has fueled the growth of outsourcing and, more specifically, Offshore Development Centers (ODCs).
The offshore software development market is projected to reach $122 billion by 2024 and a remarkable $283 billion by 2031, demonstrating the increasing reliance on this model. This article provides a comprehensive guide on what is an ODC is and how to set one up effectively.
Table of Contents
What is an ODC
An Offshore Development Center (ODC) represents a strategic partnership where a company establishes a dedicated software development team in a geographically distant country. This team operates as a seamless extension of the company’s in-house development capabilities, but with the advantage of being located in a region with different economic and talent market dynamics.
Purpose:
ODCs address several key business needs:
- Mitigating the Domestic IT Talent Shortage: Accessing a larger pool of skilled professionals beyond geographical limitations.
- Reducing Software Development Costs: Leveraging lower labor costs in other countries.
- Accessing a High-Quality Workforce at Competitive Rates: Combining cost-effectiveness with access to specialized expertise.
- Focus on Core Business Activities: By outsourcing software development to an ODC, companies can free up their internal resources and focus on their core business activities, such as product strategy, marketing, and sales. This allows for greater efficiency and focus on strategic initiatives.
- Accelerated Time to Market: With a dedicated offshore team, development can proceed at a faster pace, potentially leveraging time zone differences for round-the-clock development. This can significantly reduce time to market for new products and features.
- Scalability and Flexibility: ODCs offer greater flexibility in scaling development teams up or down as needed. This allows companies to adapt quickly to changing project requirements and market demands.
What is the difference between Onshore and Offshore
Location:
ODCs are commonly established in regions known for their strong IT talent pools and favorable business environments, such as Southeast Asian countries like Vietnam, the Philippines, India, and China, as well as Eastern Europe and parts of Latin America.
A Deep Dive into Common ODC Models
Choosing the right ODC model is a critical decision that significantly impacts the success and efficiency of your project. Understanding the nuances of each model allows you to align your choice with your specific needs and objectives. Here’s a detailed breakdown of common ODC models:
1. Dedicated Development Team:
This model provides you with a dedicated team of professionals, exclusively focused on your project. This team becomes an extension of your in-house staff, comprising developers, QA engineers, designers, and other necessary roles. You have direct control over the team or manage them through a dedicated project manager.

Pros:
- High Control and Ownership: You maintain significant control over the team’s workflow, processes, and communication, ensuring alignment with your company culture and project requirements.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Easily scale the team size up or down based on evolving project needs, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
- Strong Team Cohesion: Dedicated teams foster a strong sense of ownership and project understanding, leading to increased productivity and improved outcomes.
- Long-term Collaboration: This model facilitates building long-term relationships with your ODC team, fostering trust, shared knowledge, and efficient collaboration.
Cons:
- Higher Costs: Compared to other models, dedicated teams might have higher initial costs due to dedicated resources and infrastructure.
- Management Overhead: Requires active involvement in team management, including performance monitoring, communication, and conflict resolution.
2. Project-Based Model:
With this model, you outsource the entire project to the ODC partner. They assume full responsibility for all project phases, from requirements gathering and design to development, testing, and deployment. You define the project scope, objectives, and deliverables, while the ODC partner handles execution.
Pros:
- Reduced Management Effort: Frees you from day-to-day project management responsibilities, allowing you to focus on core business activities.
- Predictable Costs and Timelines: Clear project scope and deliverables enable better cost estimation and adherence to project timelines.
- Simplified Project Oversight: Reduces the need for constant monitoring and intervention, streamlining project oversight.
- Ideal for Well-Defined Projects: Highly suitable for projects with clear requirements and well-defined scopes.
Cons:
- Less Control: You have less direct control over the team and development process compared to the dedicated team model.
- Limited Flexibility: Changing project requirements or scope mid-project can be challenging and may incur additional costs.
- Communication Challenges: Effective communication and collaboration are crucial to ensure project success and avoid misinterpretations.
3. Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) Model:
This model involves the ODC partner building and operating a dedicated development center specifically for your needs for a defined period. After this period, the ownership and management of the ODC, including the team and infrastructure, are transferred to your company.
Pros:
- Rapid Setup: Gain quick access to a fully functional development center with established infrastructure and a trained workforce.
- Reduced Initial Investment: Minimize upfront costs associated with setting up your own ODC, allowing you to allocate resources strategically.
- Smooth Transition: The defined transfer period facilitates a seamless transition of knowledge, processes, and team management.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: Potentially achieve long-term cost savings by eventually owning and operating the ODC yourself.
Cons:
- Higher Long-Term Costs: Overall costs might be higher in the long run compared to other models due to the initial setup and operational expenses borne by the ODC partner.
- Complex Transition: Requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition of ownership and management.
- Potential for Vendor Lock-in: Choosing the right partner is crucial to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure a successful transfer.
4. Managed Service ODC Model:
This model focuses on outsourcing specific IT functions or processes to the ODC partner. They take responsibility for managing these functions, allowing you to leverage their expertise and resources while retaining control over other aspects of your project.
Pros:
- Access to Specialized Expertise: Leverage the ODC partner’s specialized skills and knowledge in specific areas, such as software testing, cloud management, or cybersecurity.
- Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings: Optimize specific processes and reduce operational costs by leveraging the partner’s resources and best practices.
- Increased Focus on Core Business: Allows your internal team to focus on strategic initiatives while the ODC partner handles specific functions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily scale the services up or down based on your evolving needs, providing flexibility and agility.
Cons:
- Vendor Dependency: Reliance on the ODC partner for specific functions can create dependencies and potential challenges if the relationship ends.
- Integration Challenges: Requires careful planning and coordination to ensure seamless integration of the outsourced functions with your existing systems and processes.
- Potential Communication Barriers: Clear communication and well-defined service level agreements are essential to avoid misunderstandings and ensure effective collaboration.
5. Hybrid Model:
This model offers the flexibility to combine elements from the above models to create a customized solution tailored to your unique needs. You can leverage the strengths of different models to optimize your project’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Pros:
- Enhanced Flexibility and Customization: Tailor the ODC model to your specific requirements, leveraging the best aspects of different approaches.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Strategically allocate resources by combining dedicated teams, project-based outsourcing, and managed services.
- Cost and Efficiency Optimization: Achieve a balance between cost savings, control, and flexibility by combining different models.
Cons:
- Increased Complexity: Managing a hybrid model can be more complex, requiring careful coordination and communication.
- Potential for Conflicts: Clear roles, responsibilities, and communication protocols are essential to avoid conflicts between different teams and models
Key Roles within an ODC:
A well-structured ODC typically includes the following roles:
- Management Team:
- Project Manager: Oversees the entire project, including business analysis, risk management, budget tracking, and communication.
- Account Manager: Maintains a strong business relationship with the client, acting as the primary point of contact.
- Business Analyst: Translates business requirements into clear technical specifications for the development team.
- Technical Team:
- Developers: Build and develop the software product, utilizing various programming languages and frameworks.
- UI/UX Designers: Design the user interface and user experience to ensure usability and visual appeal.
- Technical Writers: Create comprehensive software documentation and user manuals.
- Software Testers/QA Engineers: Ensure product quality through rigorous testing methodologies.
- Support Team:
- Human Resources: Handles recruitment, onboarding, training, and employee management.
- Administration: Manages administrative tasks such as payroll, accounting, and legal compliance.
Benefits of Setting Up an ODC:
Establishing an ODC offers numerous advantages:
- Cost Reduction: Significant savings on staffing, infrastructure, and operational costs.
- Access to Global Talent: Access a wider pool of skilled professionals with specialized expertise.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily scale the team up or down based on project demands.
- Reduced Management Burden: Delegate team management responsibilities to the outsourcing partner.
- Continuous Development and Delivery: Leverage time zone differences for 24/7 development cycles.
Challenges of Setting Up an ODC:
While ODCs offer significant benefits, it’s important to address potential challenges:
- Language and Cultural Barriers: Differences in language and work culture can create communication and collaboration hurdles.
- Maintaining Control and Oversight: Establishing clear communication channels and management processes is crucial for maintaining control.
- Time Zone Differences: Requires careful scheduling and communication strategies to bridge time gaps.
- Vendor Dependency: Choosing a reliable and long-term partner is essential to minimize risks associated with vendor transitions.
- Employee Retention: Maintaining a stable team within the ODC is important for project continuity.
How to set up Offshore Development Center
Setting up a successful ODC involves a structured approach:
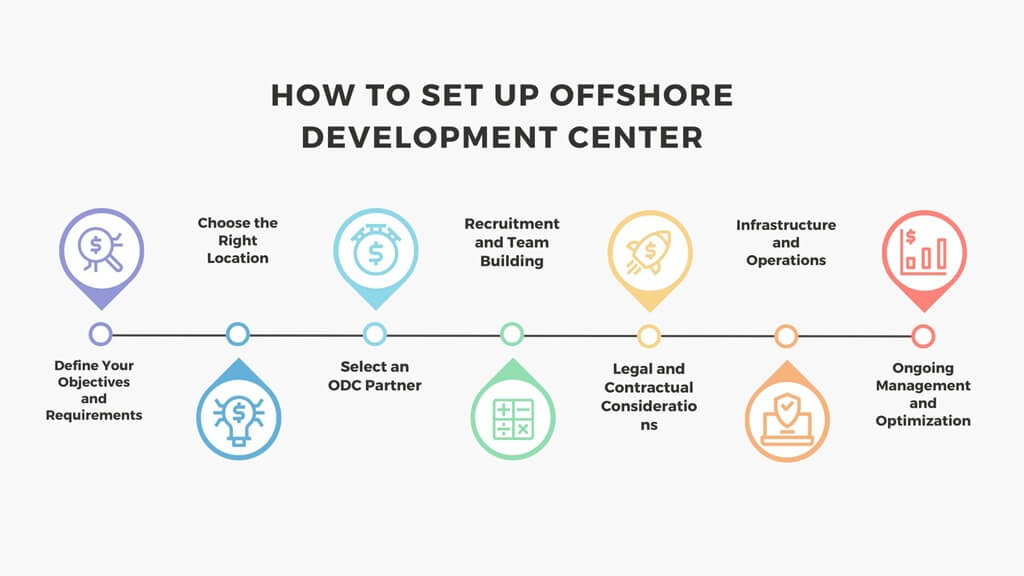
1. Define Your Objectives and Requirements:
- Project Scope and Goals: Clearly define the scope of work you intend to outsource to the ODC. Identify specific projects, ongoing development needs, or specific IT functions you want to delegate.
- Skillset Requirements: Determine the specific technical skills, experience levels, and domain expertise required for your projects.
- Team Size and Structure: Estimate the initial team size and structure, including the roles and responsibilities needed.
- Budgetary Considerations: Establish a clear budget for setting up and operating the ODC, considering factors like salaries, infrastructure costs, and operational expenses.
- Timeline and Deliverables: Define project timelines, milestones, and expected deliverables.
2. Choose the Right Location:
- Cost of Living and Labor: Analyze the cost of living and labor in potential locations to find a balance between affordability and talent quality.
- Talent Pool and Expertise: Research the availability of skilled professionals with the required expertise in your chosen technology stack.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Assess the quality of internet connectivity, power reliability, and availability of office space.
- Political and Economic Stability: Consider the political and economic stability of the country to ensure a conducive business environment.
- Time Zone Compatibility: Evaluate time zone differences and their potential impact on communication and collaboration.
- Cultural Compatibility: Assess cultural factors that may influence work styles, communication, and collaboration.
3. Select an ODC Partner:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for a partner with a proven track record in delivering similar projects and expertise in your required technologies.
- Client Testimonials and References: Check client testimonials and references to gauge the partner’s reputation and client satisfaction.
- Communication and Collaboration: Assess the partner’s communication channels, responsiveness, and willingness to collaborate effectively.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure the partner has robust security measures in place to protect your data and intellectual property.
- Transparency and Reporting: Choose a partner that provides transparent reporting on project progress, budget, and resource utilization.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Ensure the partner can adapt to your changing needs and scale the team as required.
4. Recruitment and Team Building:
- Collaborative Hiring Process: Work closely with your ODC partner to define recruitment criteria, interview candidates, and select the right talent for your team.
- Technical Assessments and Interviews: Conduct thorough technical assessments and interviews to evaluate candidates’ skills and experience.
- Cultural Fit and Communication Skills: Assess candidates’ cultural fit and communication skills to ensure effective collaboration with your in-house team.
- Onboarding and Training: Provide comprehensive onboarding and training to ensure new team members are aligned with your project goals and company culture.
5. Legal and Contractual Considerations:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Define clear SLAs with your ODC partner, outlining performance expectations, deliverables, and timelines.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Ensure that your intellectual property rights are protected through clear contractual agreements.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: Establish robust data security protocols and confidentiality agreements to protect sensitive information.
- Compliance with Local Laws: Ensure compliance with local labor laws, tax regulations, and other legal requirements in the ODC location.
- Exit Strategies: Define clear exit strategies and termination clauses in the contract to mitigate risks and ensure a smooth transition if needed.
6. Infrastructure and Operations:
- Office Space and Equipment: Provide a suitable workspace with necessary equipment, infrastructure, and technology to support your ODC team.
- Communication and Collaboration Tools: Implement effective communication and collaboration tools to facilitate seamless interaction between your in-house team and the ODC.
- Project Management Methodologies: Establish clear project management methodologies and workflows to ensure efficient project execution.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting: Implement mechanisms for monitoring team performance, tracking progress, and generating regular reports.
7. Ongoing Management and Optimization:
- Regular Communication and Feedback: Maintain open and consistent communication with your ODC team and provide regular feedback on their performance.
- Performance Reviews and Appraisals: Conduct regular performance reviews and appraisals to assess individual and team performance.
- Continuous Improvement: Identify areas for improvement in processes, communication, and collaboration to optimize ODC efficiency.
- Relationship Building: Foster a strong and collaborative relationship with your ODC partner to ensure long-term success.
ODCs are a powerful strategy for businesses seeking to leverage global talent, reduce costs, and accelerate project timelines.
Choosing the right ODC partner is paramount to success. A reliable partner will provide the necessary expertise, infrastructure, and support to ensure a smooth and efficient operation. Effective communication and management are key to maximizing the benefits of an ODC.
Axalize offers optimal offshore software development solutions with competitive pricing and exceptional quality. We provide transparent pricing structures, empowering clients to easily budget and select the right service package. Our team comprises highly experienced experts proficient in various technologies such as Java, .NET, Python, React, Angular, and has a proven track record of successfully delivering projects in diverse industries, including finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.